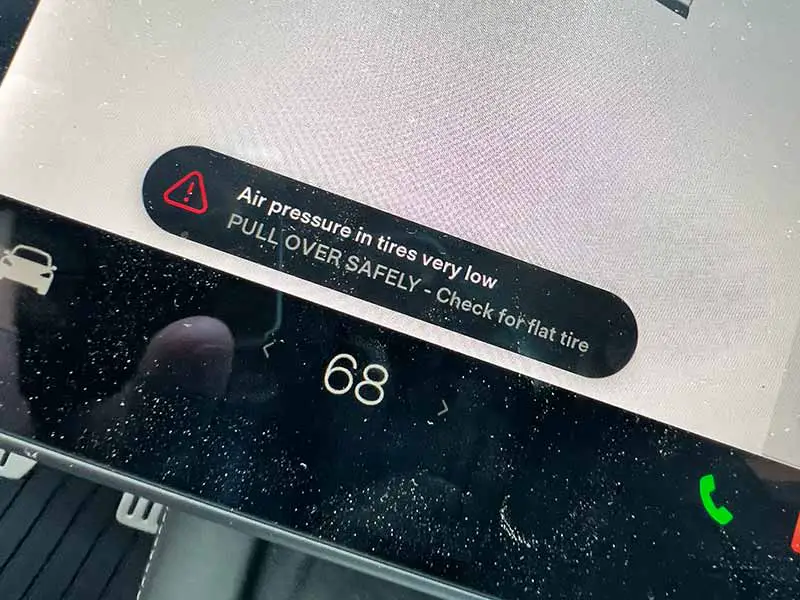
A healthy tire isn’t just about the right pressure or good treads. It’s also about the tiny TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) sensor attached to it. That small device plays a big role in your vehicle’s safety and performance.
It can seem complex, but understanding and programming a TPMS sensor isn’t rocket science. It’s a skill you can master, and we’re here to guide you.
How To Program TPMS Sensors
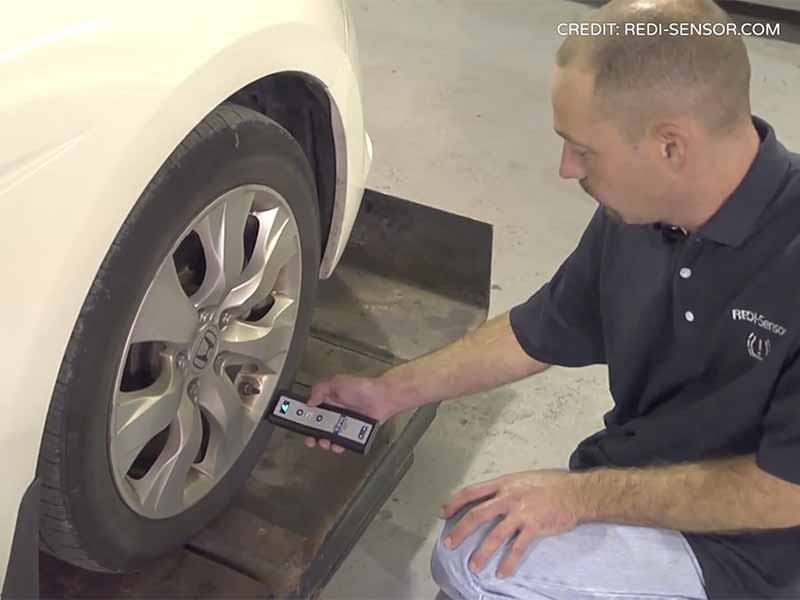
To program TPMS sensors, you’ll need a TPMS programming tool, like the Autel. This tool allows you to connect the sensor to the vehicle’s computer, input the necessary data, and confirm successful programming.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of TPMS sensors, explaining what they are and why they matter. We’ll distinguish between TPMS relearn and reprogramming, and guide you through using an Autel tool to program both Autel MX sensors and Schrader EZ-sensors.
Plus, we’ll cover cloning TPMS sensors and programming universal TPMS sensors, making sure you have the knowledge to maintain your vehicle’s TPMS system efficiently and effectively.
Let’s take a closer look.
Understanding TPMS Sensors
TPMS, short for Tire Pressure Monitoring System, is like your vehicle’s early warning system for its tires. Let’s dive deeper into what they are, why they’re so important, and the types we commonly encounter.
What are TPMS Sensors?
TPMS sensors are clever little devices installed inside your car or truck’s tires. They keep an eye on your tire pressure and send that information to your vehicle’s computer. When the pressure in one or more tires drops 25% below the recommended level, your vehicle’s dashboard flashes a warning symbol. This warning gives you time to inflate your tires before things get dangerous or costly.
Why are TPMS Sensors Important?
You might be wondering, why all this fuss over tire pressure? Well, here are a few key reasons:
- Safety: Properly inflated tires grip the road better, which means better control and fewer accidents.
- Longevity: Correct tire pressure helps your tires last longer, saving you from buying new ones ahead of schedule.
- Fuel Efficiency: Under-inflated tires make your vehicle work harder, which means it uses more gas.
Now that you know what TPMS sensors are and why they’re essential, let’s talk about the two main types you might encounter: direct and indirect TPMS sensors.
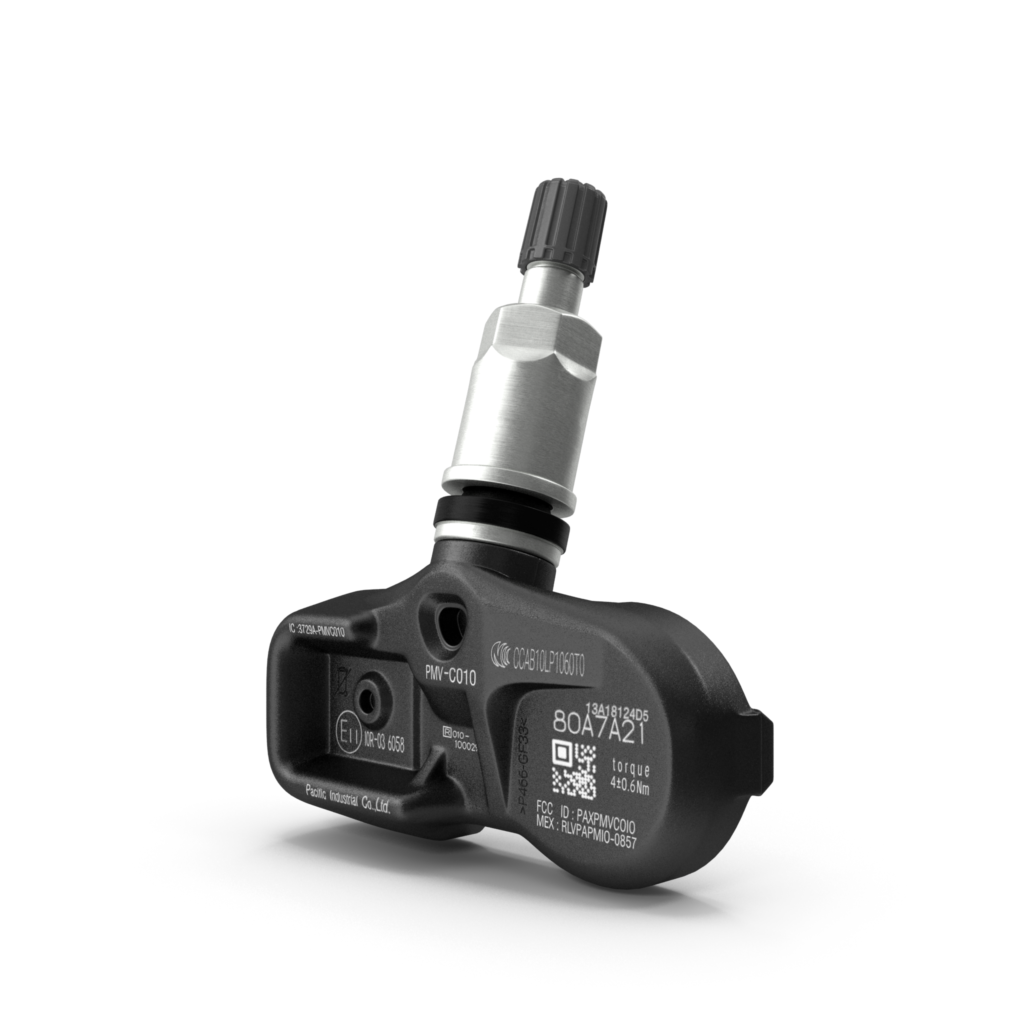

Direct TPMS Sensors
Direct TPMS sensors are located inside your tires. Each sensor measures the actual air pressure and reports it to your vehicle’s computer. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Accurate Readings: Because these sensors measure the pressure directly, their readings are very accurate.
- Battery Powered: Direct TPMS sensors are powered by batteries that usually last 5-10 years. When the battery dies, you’ll need to replace the whole sensor.
- Cost: These sensors are a bit more expensive than their indirect counterparts. However, their accuracy often outweighs the cost difference for many drivers.
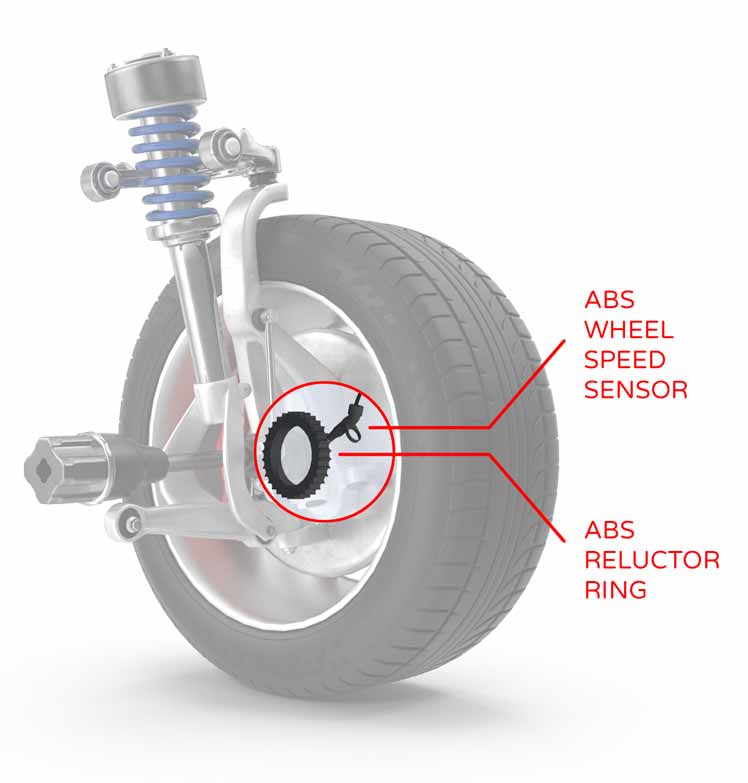
Indirect TPMS Sensors
Indirect TPMS sensors don’t measure tire pressure. Instead, they use your vehicle’s anti-lock braking system’s speed sensors to calculate tire pressure. Here’s what you need to know:
- Less Accurate: Since indirect TPMS sensors estimate the pressure based on speed sensor data, they can sometimes give inaccurate readings.
- Low Maintenance: These sensors don’t have batteries, which means less maintenance.
- Cost-Effective: Indirect sensors are less expensive than direct sensors. However, they might require more frequent checks to ensure accuracy.

Autel MX Sensor
The Basics of Programming TPMS Sensors
Programming TPMS sensors might sound intimidating, but it’s not as complicated as it seems. The process involves telling your vehicle’s computer to start communicating with the new sensors. In this section, we’ll get a handle on the basics of this process, and we’ll also talk about the tools you might need.
TPMS Programming: The Basic Steps
While the exact steps can vary depending on your vehicle model and the tools you’re using, the general process usually looks something like this:
- Step 1: Choose the Right Sensor: Not all TPMS sensors are universal. You’ll need to get a sensor that’s compatible with your vehicle.
- Step 2: Install the Sensor: Once you have the right sensor, it needs to be installed in your tire. This should typically be done by a professional to avoid damaging the tire or sensor.
- Step 3: Start the Programming: With the sensor installed, you can start the programming. This involves using a TPMS programming tool to connect the sensor to your vehicle’s computer.
- Step 4: Test It Out: After the sensor is programmed, you’ll want to test it to make sure it’s working correctly. This typically involves driving around for a bit to see if the sensor readings are accurate.
Tools You’ll Need
You’re going to need a tool to program your TPMS sensors. There are several options out there, but one commonly used tool is the Autel TPMS Programming Tool. Here’s why:
- Versatility: Autel makes tools that are compatible with a broad range of vehicles and sensors.
- Ease of Use: Autel tools are known for being user-friendly, even for beginners.
- Reliability: These tools are robust and reliable, making them a preferred choice for many.

Autel Relearn Tool
TPMS Relearn vs Reprogram
Now that you’re familiar with the basics of TPMS programming, it’s time to understand the differences between relearning and reprogramming. Though they might sound similar, they serve different purposes in the world of TPMS maintenance.
What is TPMS Relearn?
Relearning is a process your vehicle’s computer goes through to identify TPMS sensors. When you replace a sensor or rotate your tires, the computer needs to “relearn” which sensor is in which tire. Here’s what that looks like:
- Step 1: Initiate Relearn: Using a TPMS tool, initiate the relearn process. This sends a signal to the vehicle’s computer to start the process.
- Step 2: Activate Sensors: Using the TPMS tool, activate each sensor. The tool sends a signal that “wakes up” the sensor and prompts it to send a signal to the computer.
- Step 3: Confirm Completion: Once all sensors are activated, the relearn process is complete. The vehicle’s computer now recognizes each sensor in its new position.
What is TPMS Reprogram?
Reprogramming is a bit more complex. When you have a new sensor or a sensor that is not pre-programmed to your vehicle’s specific make and model, you’ll need to reprogram it. Here’s a basic rundown of what that involves:
- Step 1: Connect the Sensor and Tool: Using a TPMS programming tool, connect the tool to the sensor. This usually involves selecting the vehicle make and model on the tool and then holding the tool near the sensor.
- Step 2: Program the Sensor: The TPMS tool will provide instructions on how to program the sensor. Follow these instructions to program the sensor to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Step 3: Confirm Programming: After programming the sensor, you’ll need to confirm that the programming was successful. This typically involves driving the vehicle for a few minutes to ensure the sensor communicates properly with the computer.
Relearn vs Reprogram: The Key Differences
Now that we know what relearning and reprogramming are, let’s look at their key differences:
- Purpose: Relearning is for when the TPMS sensors are moved to different tires (like after a tire rotation), while reprogramming is for new or non-pre-programmed sensors.
- Process: The relearning process involves matching each sensor to its tire location, while the reprogramming process involves setting up the sensor to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Frequency: Relearning might need to be done more frequently (like after tire rotations or sensor battery replacements), while reprogramming typically only happens when a new or replacement sensor is installed.
How to Program TPMS Sensors with Autel
Autel’s TPMS tools are incredibly user-friendly and versatile, making them a popular choice for both professionals and DIYers. In this section, we’ll guide you through the steps to program your TPMS sensors using Autel tools. We’ll also cover programming both Autel MX TPMS sensors and Schrader EZ-Sensors with an Autel device.
Programming Autel MX TPMS Sensor
The Autel MX-Sensor is a 100% clone-able sensor that can replace 98% of direct TPMS sensors on the market today. Here’s how you program it:
- Step 1: Select Vehicle: Start by selecting the make, model, and year of your vehicle on the Autel device.
- Step 2: Connect Sensor: Place the Autel device close to the MX-Sensor and select ‘Program Sensor’.
- Step 3: Choose Programming Method: You can choose from four methods – Copy by Activation, Copy by OBD, Copy by Input, or Auto Create. Choose the one that fits your situation best.
- Step 4: Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the programming. Once done, the device will display a confirmation message.
- Step 5: Test the Sensor: Drive around for a bit to make sure the sensor is communicating correctly with the vehicle’s computer.
Programming Schrader EZ-Sensor with Autel
The Schrader EZ-Sensor is another popular programmable TPMS sensor that works well with Autel devices. Here’s how to program it:
- Step 1: Select Vehicle: On the Autel device, select the make, model, and year of your vehicle.
- Step 2: Choose Sensor: From the sensor selection menu, choose ‘Schrader EZ-Sensor’.
- Step 3: Connect Sensor: Place the Autel device near the EZ-Sensor and select ‘Program Sensor’.
- Step 4: Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the programming. You’ll see a confirmation message once the programming is successful.
- Step 5: Test the Sensor: Finally, give the sensor a test run by driving the vehicle. Make sure the sensor communicates correctly with the vehicle’s computer.

Schrader EZ Sensor
How to Clone TPMS Sensors
Cloning a TPMS sensor means creating an exact copy of the original sensor. This process can be incredibly useful, especially when replacing a damaged sensor, as it enables the new sensor to seamlessly communicate with the vehicle’s computer. Let’s explore how to clone TPMS sensors using an Autel tool.
Steps to Clone TPMS Sensors
Here’s the general process of cloning a TPMS sensor:
- Step 1: Gather Information: Start by using the Autel tool to read the original sensor’s information. This will typically include the sensor’s ID, tire location, pressure, temperature, and battery status.
- Step 2: Enter Sensor Information: Next, enter the collected sensor information into the Autel tool. This will usually involve selecting the ‘Clone Sensor’ option and then manually entering the sensor’s ID and other information.
- Step 3: Program New Sensor: With the original sensor’s information entered, you can now program the new sensor. Place the new sensor near the tool and select ‘Program Sensor’. The tool will transfer the original sensor’s information to the new sensor.
- Step 4: Confirm Successful Cloning: Once the new sensor is programmed, confirm that the cloning was successful. This usually involves checking that the new sensor’s ID matches the original sensor’s ID.
- Step 5: Install and Test: Finally, install the cloned sensor in the tire and test it. Drive around for a bit to make sure the new sensor is communicating correctly with the vehicle’s computer.
Cloning a sensor is an excellent way to maintain the same level of accuracy and reliability when you’re replacing a TPMS sensor. Since the vehicle’s computer sees the cloned sensor as the original, there’s no need for relearning or reprogramming. Just remember to always test the sensor after installation to confirm everything is working correctly.

Schrader EZ Sensor
How to Program Universal TPMS Sensor
Universal TPMS sensors, as their name implies, are designed to work with a wide variety of vehicles. These sensors can be programmed to match the specifications of your vehicle, making them a flexible option when you need to replace a TPMS sensor. Here’s how you can program a universal TPMS sensor using an Autel tool.
Steps to Program a Universal TPMS Sensor
Follow these steps to program your universal TPMS sensor:
- Step 1: Select Your Vehicle: On the Autel tool, you’ll start by selecting the make, model, and year of your vehicle.
- Step 2: Connect Sensor: Place the Autel device close to the universal TPMS sensor and select ‘Program Sensor’.
- Step 3: Choose Programming Method: The Autel tool will provide a few programming options. The method you choose depends on your specific needs. You might see options like ‘Copy by Activation’, ‘Copy by OBD’, ‘Copy by Input’, or ‘Auto Create’.
- Step 4: Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the programming. Once done, you’ll see a confirmation message on the Autel device.
- Step 5: Test the Sensor: After the sensor is installed in the tire, test it by driving the vehicle for a short period. This helps ensure the sensor is communicating accurately with the vehicle’s computer.
Programming a universal TPMS sensor allows you to replace a damaged or faulty sensor without needing to search for a specific sensor model. It can also be a great option if you’re rotating your tires and need the flexibility of a universal sensor. Remember, though, that while universal sensors can be handy, they might not offer the exact features or compatibility of an original sensor.
Resources
Below are some links you may find helpful when learning about tires
Final Thoughts
Mastering the TPMS sensor, that small but essential part of your vehicle’s safety and performance, is a skill within reach. We’ve explored what TPMS sensors are, their purpose, and how they contribute to our driving experience. We’ve also learned the distinction between relearning and reprogramming TPMS sensors, as well as the specifics of using an Autel tool to program Autel MX sensors and Schrader EZ-sensors.
Cloning a TPMS sensor allows for a seamless transition when replacing a sensor, while programming a universal TPMS sensor provides flexibility for various vehicles. By understanding these concepts and processes, you’re now equipped to ensure your vehicle’s TPMS system remains in tip-top shape. This not only improves your driving safety but also enhances overall vehicle performance. Remember, knowledge is power, and this power can save you time, money, and prevent potential tire-related accidents.
Good luck and happy motoring.





